Latest Versions of TechStack 27 Jan 2022 9:15 PM (3 years ago)
Latest Versions of TechStack
| Software | Used Version(s) | Current |
|---|---|---|
| Java | 8,13 | Java SE 17 (LTS) |
| Spring boot | 2.3.12 | 2.6.3 |
| Angular | NA | 13.1.1 |
| Android studio | NA | 4.1 |
| Lombok | v1.17 | v1.18.22 |
| Log4j 2 | 2.17.1 | 2.17.1 |
| Oracle | 12 | 19c |
| Springfox swagger | 2.9.2 | 3.0.0 |
| Resiliance 4j | 1.7 | 1.7.1 |
| Jenkins | 2.324 | 2.324 |
Apache Kafka - FAQs 28 Nov 2019 3:39 PM (5 years ago)
Apache Kafka : an open-source message broker project developed by the Apache Software Foundation written in Scala and is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system.
Features of kafka
High Throughput : Support for millions of messages with modest hardware
Scalability : Highly scalable distributed systems with no downtime
Replication : Messages are replicated across the cluster to provide support for multiple subscribers and balances the consumers in case of failures
Durability Provides support for persistence of message to disk
Stream Processing Used with real-time streaming applications like Apache Spark & Storm
Data Loss Kafka with proper configurations can ensure zero data loss
Various components of Kafka:
Topic – a stream of messages belonging to the same type
Producer – that can publish messages to a topic
Brokers – a set of servers where the publishes messages are stored
Consumer – that subscribes to various topics and pulls data from the brokers.
Topic :
Topic is like a table identified by name.
Topic is split in partitions.
Topic 1 -- Partition 0, partition 1 , partition 2.
Explain the role of the offset.
Messages contained in the partitions are assigned a unique ID number that is called the offset. The role of the offset is to uniquely identify every message within the partition.
- kafka stores offsets at which consumer group has been reading.
- offsets will be stored in a separate topic called "_consumer_offsets"
- When consumer has processed data received from kafka it should be committing the offsets.
- offset is specific to a partition. because offset 3 in partion 1 and 2 are not same.
- offset is in order with in a partition.
- data / offsets kept only for one week by default.
- once data written cant be changed (immutable)
- Data is assigned randomly to a partition if we dont specify key
What is a Consumer Group?
To enhance parallelism.
Consumer Groups is a concept exclusive to Kafka. Every Kafka consumer group consists of one or more consumers that jointly consume a set of subscribed topics.
You cant have more consumers than partitions.
if you have 3 partitions u should not have 4 consumers in one group. because consumers in a group shares the partitions. if we have 3 partitions for a topic and 4 consumers in a group each consumer connects to one partitions and 4th one become idle and do nothing.
consumer has to specify broker name and topic name to read and kafka will take care of pulling data from right brokers
Messages are read in order like 0,1,2,... but in parallel across the partitions.
B1 - Topic 1 - partition 0 - 0,1,2,3,4
B2 - Topic 2 - partition 1 - 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
Each consumer within a group read from exclusive partitions.
Brokers
- A Kafka cluster is composed of multiple brokers(servers)
- Each broker contains certain topic partitions.
- After connecting to any broker , you will be connected to entire cluster.
- A cluster with 3 brokers can be seen as follows , data is distributed with partitions.
Broker 1 Broker 2 Broker 3
Topic 1 Topic 1 Topic 1
P-0 P-2 P-1
Topic 2 Topic 2 Topic 1
P-1 P-0 P-0
Replication Factor always > 1
Partitions :
- Partitions are the main concurrency mechanism in kafka.
- A topic is divided into 1 or more partitions enabling producer and consumer loads to be scaled.
What is the role of the ZooKeeper?
Kafka uses Zookeeper to store offsets of messages consumed for a specific topic and partition by a specific Consumer Group.
Is it possible to use Kafka without ZooKeeper?
No, it is not possible to bypass Zookeeper and connect directly to the Kafka server. If, for some reason, ZooKeeper is down, you cannot service any client request.
Explain the concept of Leader and Follower.
Every partition in Kafka has one server which plays the role of a Leader, and none or more servers that act as Followers. The Leader performs the task of all read and write requests for the partition, while the role of the Followers is to passively replicate the leader. In the event of the Leader failing, one of the Followers will take on the role of the Leader. This ensures load balancing of the server.
Why are Replications critical in Kafka? Kafka is durable with replications.
Replication ensures that published messages are not lost and can be consumed in the event of any machine error, program error or frequent software upgrades.
How do you define a Partitioning Key?
Within the Producer, the role of a Partitioning Key is to indicate the destination partition of the message. By default, a hashing-based Partitioner is used to determine the partition ID given the key. Alternatively, users can also use customized Partitions.
New Features in Java 13 13 Nov 2019 8:04 PM (5 years ago)
New Features in Java 13
- We initially saw switch expressions in JDK 12 itself, build on the previous version by adding a new yield statement.
- Text Blocks - To embed JSON , XML etc to avoid escaping in the strings.
- Class data sharing (CDS)
- ZGC: Uncommit Unused Memory
- Reimplement the Legacy Socket API
GIT Eclipse usage basic 2 Aug 2017 7:10 AM (8 years ago)
- create a new repository : create a new directory, open it and perform a
- git init
- checkout a repository : Create a working copy of a local repository by running the command
- git clone /path/to/repository
- Goto project dir
2. git status
3.git add .
4. git status
5. git commit -m "first commit"
6. Create an empty repo in GITHUB
7.copy clone url
8.git remote add origin << URL >>
9.git push -u origin master
10. Check your files are there on GIT remote
To add more / update files
- git add .
- git status
- git commit -m "second commit"
- git push -u origin master
Static keyword in java 26 Feb 2017 9:28 PM (8 years ago)
Static keyword in java
- Variable
- Method
- Block
- Class
1. Static variable in Java
- Static variables are also known as a class variable because they are associated with the class and common for all the objects of a class.
- Static variables are declared using the static keyword within a class outside any method/constructor/block.
- When a class created then one copy of a static variable created in memory. Static variables would be common for all objects of class because a static variable is associated with a class.
- Static variables are created at the start of program execution and destroyed automatically when execution ends.
- Initialization of Static Variable is not Mandatory. Its default value is depending on the data type of variable.
- If we access the static variable through an object the compiler will show the warning message. The compiler will replace the object name to the class name automatically.
- We can create static variables at class-level only.
2. Static method in Java
2. You can access a static method by using the class name. You do not have the need to create an object.
3. A static method can access only static variables. If you write any non-static variable in a static method, then it will throw an exception at compilation time.
3. Static block in Java
4. Static class in Java
Krishna babu Ghanta
Spring architecture and Spring boot 26 Feb 2017 8:21 PM (8 years ago)

Spring AOP
One of the key components of Spring is the AOP framework. AOP is used in Spring:
To provide declarative enterprise services, especially as a replacement for EJB declarative services. The most important such service is declarative transaction management, which builds on Spring’s transaction abstraction.
To allow users to implement custom aspects, complementing their use of OOP with AOP
Spring ORM
The ORM package is related to the database access. It provides integration layers for popular object-relational mapping APIs, including JDO, Hibernate and iBatis.
Spring Web
The Spring Web module is part of Spring?s web application development stack, which includes Spring MVC.
Spring DAO
The DAO (Data Access Object) support in Spring is primarily for standardizing the data access work using the technologies like JDBC, Hibernate or JDO.
Spring Context
This package builds on the beans package to add support for message sources and for the Observer design pattern, and the ability for application objects to obtain resources using a consistent API.
Spring Web MVC
This is the Module which provides the MVC implementations for the web applications.
Spring Core
The Core package is the most import component of the Spring Framework.
This component provides the Dependency Injection features. The BeanFactory provides a factory pattern which separates the dependencies like initialization, creation and access of the objects from your actual program logic.
Java Springboot Microservices FAQs 26 Feb 2017 6:45 PM (8 years ago)

- Is Spingboot thread-safe?
It depends. The main factor which determines the thread-safety of a component is its scope.
In a standard servlet-based Spring web application, every new HTTP request generates a new thread. If the container creates. a new bean instance just for that particular request, we can say this bean is thread-safe.
Is Spring singleton thread-safe?
The short answer is: no, it isn't.
Reference: http://dolszewski.com/spring / spring-bean-thread-safety-guide /
- Different scopes of beans ?
- singleton : Singleton is the default scope for a Bean
- prototype
- request
- session
- application
- websocket
- What are the disadvantages of Springboot?
- What are different design patterns you use in the Microservices ?
- How do we implement spring security?
start by creating a Spring Security configuration class that extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter . By adding @EnableWebSecurity, we get Spring Security and MVC integration support.
rest security
security config class-
basic auth
authentication filter-> authentication object-> not validated-> authentication manager builder->
finds authetication providers-> like DAO or custom authentication provider
we can pass JWT token in header for authentication.
server validates if it is generated by itself.
session-based vs token based security.
tokens are stateless
requests can go to any node which doesn't understand previous session settings.
What is Bearer (ur the owner of the token) Vs Basic
after authentication is done only we get JWT token which is used for authorization
JWT --OAUTH Grant Types:
implicit --Implicit Grant
authorization_code --Authorization Code Grant- This grant type flow is also called "three-legged" OAuth.
You've seen this flow anytime your app opens a browser to the resource server's login page and invites you log in to your actual account (for example, Facebook or Twitter).
If you successfully log in, the app will receive an authorization code that it can use to negotiate an access token with the authorization server.
client_credentials --Client Credentials Grant
password --Resource Owner Password Grant
refresh_token --Use Refresh Tokens
urn: ietf: params: oauth: grant-type: device_code --Device Authorization Grant
Reference: https://developer.okta.com/blog/2018/10/05/build-a-spring-boot-app-with-user-authentication
3. How to cancel an order for user-specific settings at the spring level?
3b. Multi calls between ms to ms?
Using discovery services like Eureka we can route calls between internal microservices effectively.
- How do we resolve cyclic dependency issues in Springboot?
By using @Lazy annotation on the dependency we can resolveor avoid constructor based injection in SB and use setter based injection
- Tomcat Max Threads settings in Springboot application?
server.tomcat.max-connections | 8192 |
Maximum number of connections that the server accepts and processes at any given time. Once the limit has been reached, the operating system may still accept connections based on the "acceptCount" property.
|
server.tomcat.max-http-form-post-size | 2MB |
Maximum size of the form content in any HTTP post request.
|
server.tomcat.max-swallow-size | 2MB |
Maximum amount of request body to swallow.
|
server.tomcat.max-threads | 200 |
Maximum amount of worker threads.
|
server.tomcat.mbeanregistry.enabled | false |
Whether Tomcat's MBean Registry should be enabled.
|
server.tomcat.min-spare-threads | 10 |
Minimum amount of worker threads.
|
server.tomcat.port-header | X-Forwarded-Port |
Name of the HTTP header used to override the original port value.
|
server.tomcat.processor-cache | 200 |
Maximum number of idle processors that will be retained in the cache and reused with a subsequent request. When set to -1 the cache will be unlimited with a theoretical maximum size equal to the maximum number of connections.
|
server.tomcat.protocol-header |
Header that holds the incoming protocol, usually named "X-Forwarded-Proto".
|
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/appendix-application-properties.html
- Sort Employee salary using Java Streams and display salary which is greater than X amount? Java 8 --streams, lambda expression
// find employees whose salaries are above 10000 empList.stream().filter(emp->emp.getSalary() > 10000).forEach(System.out::println);Reference:
https://www.java2novice.com/java-8/streams/filter-method-example/
- Spring boot --Dependency injection types?
There are basically three types of dependency injection:
constructor injection: the dependencies are provided through a class constructor.
setter injection: the client exposes a setter method that the injector uses to inject the dependency.
Interface injection: the dependency provides an injector method that will Clients must implement an interface that exposes a setter method that accepts the dependency.
So now its the dependency injection's responsibility to:
- Create the objects
- Know which classes require those objects
- And provide them all those objects
- How do we do monitoring of REST APIS ?
- How do we call External Microservices in Springboot REST APIS ?
Resttemplate : getForEntity(gets full responseEntity) vs getForObject (only object we get)
exchange also do the same
- What are status codes for DELETE API ?
Right Status codes for delete - 204 - content not found
200 - OK
- Why Do we need Timeout setting in REST APIs ?
For each request, a thread is blocked.
at one point in time threads will be out. so time out is needed to release threads. Default is 200 threads in thread pool.
Ex :Read time out(not able to complete reading data) , server time out (not able to get connection)
- Versioning in REST APIs ?
the new functionality will be rolled with new version apis
using request param or path param
also using headers
uri @Getmapping
- What is content negotiation in the REST ?
mediatype : Produces or consumes is nothing but content negotiation.
- What are cross-cutting concerns?
AOP - for logging purposes,
security setup using Request Filters, and Interceptors for managing requests and response data
- How do you create custom annotation in spring boot?
STEP1: Create an interface with the annotation name
STEP2: Create an Aspect
STEP3: Add the annotation
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Traceable {
}
- Pagination and Sorting using Spring Data JPA
public interface ProductRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Product, Integer> {
List<Product> findAllByPrice(double price, Pageable pageable);
}
Conversely, we could have chosen to extend JpaRepository instead, as it extends PagingAndSortingRepository too.
HATEOAS constraint of REST means enabling the client of the API to discover the next and previous pages based on the current page in the navigation.
we're going to use the Link HTTP header, coupled with the “next“, “prev“, “first” and “last” link relation types.
In the case of pagination, the event – PaginatedResultsRetrievedEvent – is fired in the controller layer. Then we'll implement discoverability with a custom listener for this event.
- REST Controller
@Api
@RequestMapping("/v1")
public interface ProfileV1Interface{
@ApiOperation(value = "Api to Get a specific setting for a cluster", notes = "Get a specific setting for a Cluster")
@GetMapping(value = "/cluster/{name}/settings", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
Map<String, String> getClusterSetting(@RequestParam(required = true) String clusterId,@PathVariable(required = true) String name);
}
- @autowire Vs @Inject
@Autowired is Spring's own annotation. @Inject is part of a Java technology called CDI that defines a standard for dependency injection similar to Spring. In a Spring application, the two annotations work the same way as Spring has decided to support some JSR-299 annotations in addition to their own.
- Tell me some important annotations in springboot?
@Controller: The @Controller is a class-level annotation. It is a specialization of @Component. It marks a class as a web request handler. It is often used to serve web pages. By default, it returns a string that indicates which route to redirect. It is mostly used with @RequestMapping annotation.
JBOSS start and stop shell scripts - domain mode - host controller - domain controller 22 Feb 2017 1:45 PM (8 years ago)
===========START DOMAIN CONTROLLER MACHINE JBOSS=================
echo "Setting JBOSS Env"
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/app/java/jdk/jdk160
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/app/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
echo "PATH is : $PATH"
echo "JBOSS Environment is ready and starting jboss in domain mode"
echo "MY:JAVA_OPTS: $JAVA_OPTS"
export JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -DASOCPropsFile=/abc/etc/abc.props -DLNSPropsFile=/pns/etc/pns.props -DAVSPropsFile=/bvs/etc/bvs.props -DEOTPropsFile=/toe/etc/toe.props -DLPSPropsFile=/psl/etc/psl.props -DADLPropsFile=/hfl/etc/hfl.props -Dcom.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.client.HttpTransportPipe.dump=true"
echo "MY AFTER:JAVA_OPTS: $JAVA_OPTS"
/export/opt/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3/bin/domain.sh -b cldv0015.abc.cpf.com -bmanagement cldv0015.abc.cpf.com &
=============================================
============START HOST CONTROLLER==========
=============================================
==========STOP JBOSS Process harshly==============
echo "Stopping JBOSS JAVA processes"
for i in `ps -eaf | grep jboss | grep java | cut -d " " -f6`
{
kill -9 $i
echo "Killing: $i"
}
ps -eaf | grep jboss | grep java
echo "Stop completed"
============================================
Unix command to find class in jar | windows command to search class in jars 29 Jul 2016 12:52 PM (9 years ago)
Unix :
find . -type f -name '*.jar' -print0 | xargs -0 -I '{}' sh -c 'jar tf {} | grep com/sun/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class && echo {}'
find . -type f -name '*.jar' -print0 | xargs -0 -I '{}' sh -c 'jar tf {} | grep HostnameVerifier.class && echo {}'
Ex :
[kg6378@bldv0014 jdk1.6.0_20]$ find . -type f -name '*.jar' -print0 | xargs -0 -I '{}' sh -c 'jar tf {} | grep com/sun/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class && echo {}'
com/sun/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class
./jre/lib/jsse.jar
[kg6378@bldv0014 jdk1.6.0_20]$ find . -type f -name '*.jar' -print0 | xargs -0 -I '{}' sh -c 'jar tf {} | grep HostnameVerifier.class && echo {}'
com/sun/deploy/security/CertificateHostnameVerifier.class
./jre/lib/deploy.jar
javax/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class
javax/net/ssl/HttpsURLConnection$DefaultHostnameVerifier.class
sun/net/www/protocol/https/DefaultHostnameVerifier.class
com/sun/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class
./jre/lib/jsse.jar
Windows :
forfiles /S /M *.jar /C "cmd /c jar -tvf @file | findstr /C:"HostnameVerifier.class" && echo @path"
C:\Users\kg6378\Desktop\jdk-7u79-windows-x64\tools>cd C:\Krish\MyDocs\SWS\Jdk1.6
.0_14
C:\Krish\MyDocs\SWS\Jdk1.6.0_14>forfiles /S /M *.jar /C "cmd /c jar -tvf @file |
findstr /C:"HostnameVerifier.class" && echo @path"
3517 Thu May 21 09:19:20 EDT 2009 com/sun/deploy/security/CertificateHostnameV
erifier.class
"C:\Krish\MyDocs\SWS\Jdk1.6.0_14\jre\lib\deploy.jar"
194 Thu Feb 05 13:54:20 EST 2009 javax/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class
618 Thu Feb 05 13:54:22 EST 2009 javax/net/ssl/HttpsURLConnection$DefaultHost
nameVerifier.class
384 Thu Feb 05 13:54:22 EST 2009 sun/net/www/protocol/https/DefaultHostnameVe
rifier.class
272 Thu Feb 05 13:54:32 EST 2009 com/sun/net/ssl/HostnameVerifier.class
"C:\Krish\MyDocs\SWS\Jdk1.6.0_14\jre\lib\jsse.jar"
C:\Krish\MyDocs\SWS\Jdk1.6.0_14>
JBOSS - Profiles - socket binding - offset - Groups - Server 22 Sep 2015 8:19 AM (10 years ago)
In JBOSS above are some common yet important terminology.
Each Server instance will fall under a group. It can follow its own socket binding.
Each group falls under a profile. Default , Full , Full-has etc
Based on socket binding default HTTP port and server offset we need to find out the server running http port.
Caused by: org.jboss.modules.xml.XmlPullParserException: Failed to add resource root 'abc.jar' at path 'abc.jar' (position: END_TAG seen ... 17 Sep 2015 7:54 AM (10 years ago)
Caused by: org.jboss.modules.xml.XmlPullParserException: Failed to add resource root 'abc.jar' at path 'abc.jar' (position: END_TAG seen ...
at org.jboss.modules.ModuleXmlParser.parseResourceRoot(ModuleXmlParser.java:723) [jboss-modules.jar:1.3.3.Final-redhat-1]
at org.jboss.modules.ModuleXmlParser.parseResources(ModuleXmlParser.java:572) [jboss-modules.jar:1.3.3.Final-redhat-1]
at org.jboss.modules.ModuleXmlParser.parseModuleContents(ModuleXmlParser.java:394) [jboss-modules.jar:1.3.3.Final-redhat-1]
at org.jboss.modules.ModuleXmlParser.parseDocument(ModuleXmlParser.java:219) [jboss-modules.jar:1.3.3.Final-redhat-1]
at org.jboss.modules.ModuleXmlParser.parseModuleXml(ModuleXmlParser.java:153) [jboss-modules.jar:1.3.3.Final-redhat-1]
... 18 more
Solution : This is just because your global module jar file is corrupted and can not be read. Delete and copy the jar properly.
More similar error :
09:38:16,093 ERROR [org.jboss.msc.service.fail] (MSC service thread 1-4) MSC000001: Failed to start service jboss.module.service."deployment.TestWebProj.war".main: org.jboss.msc.service.StartException in service jboss.module.service."deployment.TestWebProj.war".main: JBAS018759: Failed to load module: deployment.TestWebProj.war:main
at org.jboss.as.server.moduleservice.ModuleLoadService.start(ModuleLoadService.java:91) [jboss-as-server-7.4.0.Final-redhat-19.jar:7.4.0.Final-redhat-19]
at org.jboss.msc.service.ServiceControllerImpl$StartTask.startService(ServiceControllerImpl.java:1980) [jboss-msc-1.1.5.Final-redhat-1.jar:1.1.5.Final-redhat-1]
at org.jboss.msc.service.ServiceControllerImpl$StartTask.run(ServiceControllerImpl.java:1913) [jboss-msc-1.1.5.Final-redhat-1.jar:1.1.5.Final-redhat-1]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.runTask(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:895) [rt.jar:1.6.0_95]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:918) [rt.jar:1.6.0_95]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:682) [rt.jar:1.6.0_95]
JBOSS : WARs deployment shell script 16 Sep 2015 8:12 AM (10 years ago)
---------Script 1 invokes script 2 and creates a log file---------
#!/bin/sh
datestr=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
./connectToCLLI.sh > AsocDeploymentLog_$datestr
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
----------SCRIPT 2 , reads props file and get the WAR file and Group information-------
#!/bin/ksh
echo "Setting JBOSS Env"
export JBOSS_HOME=/export/opt/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/app/java/jdk/jdk160
export PATH=$PATH:$JBOSS_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
export JB_CLI=$JBOSS_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh
DEPLOYMENT_HOST=`nslookup \`hostname\` |grep Name | awk '/:/{print $2}'`
export HOME_DIR=/pbcf/ctfr1603/
echo "JBOSS Environment is ready and connecting to CLLI"
allDeployed=0
for LINE in `cat deploymentDescABC.props | grep -v "#"`
{
VAL1=`echo $LINE |cut -d '|' -f1 `
GROUPS=`echo $LINE |cut -d '|' -f2 `
export WAR_FILE=$HOME_DIR$VAL1
echo "Deploying $WAR_FILE now"
#export COMMANDS="connect,deploy $WAR_FILE --force,quit"
export COMMANDS="connect,deploy $WAR_FILE --server-groups=$GROUPS,quit"
echo "COMMANDS is $COMMANDS"
if $JB_CLI -c --controller=$DEPLOYMENT_HOST:9999 --commands="$COMMANDS"
then
echo "Deployment successful for $WAR_FILE !!"
else
echo "Deployment failed for $WAR_FILE "
allDeployed=1
break
fi
}
if [ $allDeployed = "0" ]
then
echo "Overall deployment of all WARs is successful"
else
echo "Overall deployment FAILED !!"
fi
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------Sample Props file -------------
# list of WARs for ASOC Module
/abc/def/MyTestwar|G2
/abc/def/YourTestwar|G2
All WARs done#
----------------------------------------------
Sample Deploy and undeploy commands :
[jboss@hex0015 bin]$ ./jboss-cli.sh --controller=hex0015.abc.com:9999
You are disconnected at the moment. Type 'connect' to connect to the server or 'help' for the list of supported commands.
----------------------------
[disconnected /] connect
[domain@hex0015.abc.com:9999 /] deploy /ssd/etc/jboss_config/atp/csac/PressQuery.war --all-server-groups
[domain@hex0015.abc.com:9999 /] undeploy PressQuery.war --all-relevant-server-groups
JBOSS - Global modules - profiles modules.xml 10 Sep 2015 7:49 AM (10 years ago)
To used jboss global modules we need to writed module.xml with list of jars under
/export/opt/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3/modules/
Example : /export/opt/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3/modules/com/abc/main/module.xml
After having this module.xml and copying the required jars into dir :
/export/opt/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3/modules/com/abc/main
We need to add entry to the
domain.xml
But this is very important to add under rite profile. For example if you want to share these global modules under default profile your servers also should fall under the same default profile.
If you server exists under a group which follows full profile you should have this entry in the full profile.
ERROR [org.jboss.modcluster] (ContainerBackgroundProcessor[StandardEngine[jboss.web]]) MODCLUSTER000042: Error null sending INFO command to zldv7606.vci.att.com/135.49.207.238:6666, configuration will be reset: null 8 Sep 2015 7:36 AM (10 years ago)
ERROR [org.jboss.modcluster] (ContainerBackgroundProcessor[StandardEngine[jboss.web]]) MODCLUSTER000042: Error null sending INFO command to zldv7606.vci.att.com/135.49.207.238:6666, configuration will be reset: null
Solution :
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/app/java/jdk/jdk160/bin
bldv0014:/opt/app/jboss/jboss-eap-6.3/bin> ./jboss-cli.sh --controller=abcd0015.cddef.pbc.com:9999
You are disconnected at the moment. Type 'connect' to connect to the server or 'help' for the list of supported commands.
[disconnected /] connect
Authenticating against security realm: ManagementRealm
Username: jbadmin
Password:
[domain@abcs0015.cdef.pbc.com:9999 /] /profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster:remove
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => undefined,
"server-groups" => undefined
}
How to print request and response XML data (HTTP communication information) in JBOSS server logs ? 3 Sep 2015 7:39 AM (10 years ago)
Set the below property to JVM process being run for jboss
-Dcom.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.client.HttpTransportPipe.dump=true
Webservice HTTPS client running - SSL handshake confirmation - print SOAP request response data 2 Sep 2015 7:30 AM (10 years ago)
-Djavax.net.debug=ssl
Sample run command :
java -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/spl/etc/iscks.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=csi123 -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=/lps/etc/iscks.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=csi123 -Djavax.net.debug=ssl spl.isc.ISCWebServiceClient
And another common problem is that we want to see how soap request and response is happening .
in such case use the below java code in the client to see how soap request and response happens
-Djavax.net.debug=ssl
Other way : with in java client code.
System.setProperty("com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.client.HttpTransportPipe.dump", "true");
System.setProperty("com.sun.xml.internal.ws.transport.http.client.HttpTransportPipe.dump", "true");
System.setProperty("com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.HttpAdapter.dump", "true");
System.setProperty("com.sun.xml.internal.ws.transport.http.HttpAdapter.dump", "true");
JDK Version history - Best Features 16 Apr 2014 1:45 AM (11 years ago)
Creating Web-Service Client for online webservices using AXIS2 16 Apr 2014 12:59 AM (11 years ago)
First we should know who is providing on-line web-services(WS).
http://www.webservicex.net is one such site where we can find different on-line web-services like Stock Quote, IP Locator etc.
We can see WSDL file for each WS in the above site and using this WSDL we need to generate our client and to query the WS .
We can send request to the on-line Web-service and in turn we get response for the request from WS .
So For example if we have generated Stock Quote WS client code , in request we send a symbol (for EX: IBM) to request it's recent stock quote value.
So in response we should get it's latest value and other stuff.
Before we generate WS Client code for provided WSDL in Stock quote from http://www.webservicex.net .
Let's see how it works
SOAP UI is one of the easiest way to check this out.
Download SOAP UI ZIP and launch the SOAP UI . http://sourceforge.net/projects/soapui/files/soapui/5.0.0/SoapUI-5.0.0-windows-bin.zip/download
After extracting you can run file : soapui.bat from it's extracted location Webservices_Stuff\SoapUI-5.0.0\bin
Create a new project for example StockQuote in SOAPUI and provide WSDL path taken from http://www.webservicex.net for Stock Quote
WSDL used :
http://www.webservicex.net/stockquote.asmx?WSDL
On the left hand side in the SOAPUI new project is created with GetQuote and Request 1 etc.
If we double click the Request 1 we will see a window opened with two parts one with Request XML and other one Response XML.
There in the Request XML if set the ? symbol with IBM like one company symbol and click on run button on the top it gives us the response with
detailed information on the stock.
So now our next job is to create client code for the StockQuote in our eclipse .
So first let's download the AXIS2 project to help on this.
Download axis2-1.6.2-war.zip , from http://archive.apache.org/dist/axis/axis2/java/core/1.6.1/axis2-1.6.1-war.zip
And Create a user library to hold the required jars in path ...
Look for screenshot attached.
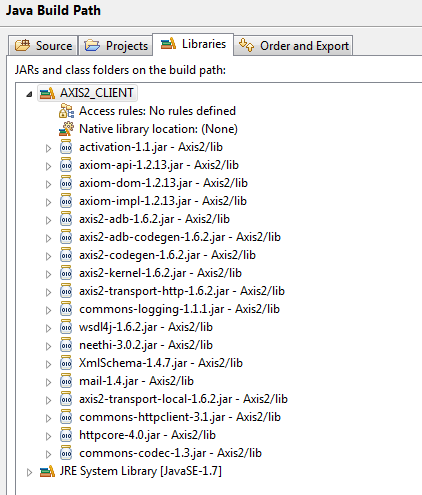
Now create a java project with name StockQuote and From Eclipse Run > RunConfigurations create new StockQuote run configuration.
In the main tab provide Project name as StockQuote and provide main class as
org.apache.axis2.wsdl.WSDL2Java
In the Arguments tab
under Program arguments
provide required arguments like
-o C:\Krish\MyDocs\WorkSpaces\My_Java_Workspace\StockQuote
-p com.demo.ws.stock.quote
-u
-uri http://www.webservicex.net/stockquote.asmx?WSDL
Now run this Run Configuration
Refresh the StockQuote Project from left navigation on Eclipse.
Now You should see new code file created for StockQuote Web-Service Client under Src directory.
Observe StockQuoteStub.java file.
to find out how to construct Request and Response objects
Now write your main client class ... sample file looks like below ..
Sample Main Code :
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import net.webservicex.www.GetQuote;
import net.webservicex.www.GetQuoteResponse;
import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault;
import com.demo.ws.stock.quote.StockQuoteStub;
public class MainClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException {
try {
StockQuoteStub stub = new StockQuoteStub();
GetQuote gq = new GetQuote();
gq.setSymbol("IBM");
GetQuoteResponse resp = stub.getQuote(gq);
System.out.println(resp.getGetQuoteResult());
} catch (AxisFault e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Sample Output after running this WS : Sorting algorithms in java array 18 Feb 2014 1:56 AM (11 years ago)
let's see how these searching algorithms can be implemented in Java using arrays.
Below are the implemented searching algorithms in the below example code.
- Implement bubble sort in java.
- Implement selection sort in java.
- Implement insertion sort in java.
- Implement quick sort in java.
- Implement merge sort in java.
package com.krish.sorting;
import java.util.Random;
public class SortingTechniques {
// Applies selection sort technique to the given array
public static int[] doSelectionSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[index]) {
index = j;
}
}
int smallerNumber = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[i];
arr[i] = smallerNumber;
}
return arr;
}
// Applies bubble sort technique to the given array
public static int[] doBubbleSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
int k;
for (int m = n; m >= 0; m--) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
k = i + 1;
if (arr[i] > arr[k]) {
swapNumbers(i, k, arr);
}
}
}
return arr;
}
// Applies Insertion sorting Technique
public static int[] doInsertionSort(int[] arr) {
int temp;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
// Applies Quick sort to the given array
public static void doQuickSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex,int[] myArray) {
int i = lowerIndex;
int j = higherIndex;
// calculate pivot number, I am taking pivot as middle index number
int pivot = myArray[lowerIndex + (higherIndex - lowerIndex) / 2];
// Divide into two arrays
while (i <= j) {
/**
* In each iteration, we will identify a number from left side which
* is greater then the pivot value, and also we will identify a
* number from right side which is less then the pivot value. Once
* the search is done, then we exchange both numbers.
*/
while (myArray[i] < pivot) {
i++;
}
while (myArray[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
exchangeNumbers(i, j,myArray);
// move index to next position on both sides
i++;
j--;
}
}
// call quickSort() method recursively
if (lowerIndex < j)
doQuickSort(lowerIndex, j,myArray);
if (i < higherIndex)
doQuickSort(i, higherIndex,myArray);
}
private static void exchangeNumbers(int i, int j,int[] myArray) {
int temp = myArray[i];
myArray[i] = myArray[j];
myArray[j] = temp;
}
private static void swapNumbers(int i, int k, int[] arr) {
int temp;
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[k];
arr[k] = temp;
}
public static void printArray(int[] printArray) {
for (int i : printArray) {
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
private static int[] getRandomNumbersArray() {
Random myRandom = new Random();
int[] randomArray = { myRandom.nextInt(100), myRandom.nextInt(20),
myRandom.nextInt(600), myRandom.nextInt(60),
myRandom.nextInt(200) };
return randomArray;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] myArray = getRandomNumbersArray();
System.out.println("\nBefore Selection sort:");
printArray(myArray);
System.out.println("\nAfter Selection sort:");
printArray(doSelectionSort(myArray));
myArray = getRandomNumbersArray();
System.out.println("\nBefore Bubble sort:");
printArray(myArray);
System.out.println("\nAfter Bubble sort:");
printArray(doSelectionSort(myArray));
myArray = getRandomNumbersArray();
System.out.println("\nBefore Insertion sort:");
printArray(myArray);
System.out.println("\nAfter Insertion sort:");
printArray(doSelectionSort(myArray));
myArray = getRandomNumbersArray();
System.out.println("\nBefore Quick sort:");
printArray(myArray);
int length = myArray.length;
doQuickSort(0, length - 1,myArray);
System.out.println("\nAfter Quick sort:");
printArray(myArray);
}
}
Output : Before Selection sort:
10, 0, 480, 41, 175,
After Selection sort:
0, 10, 41, 175, 480,
Before Bubble sort:
77, 3, 91, 4, 8,
After Bubble sort:
3, 4, 8, 77, 91,
Before Insertion sort:
35, 14, 41, 24, 168,
After Insertion sort:
14, 24, 35, 41, 168,
Before Quick sort:
6, 9, 188, 21, 102,
After Quick sort:
6, 9, 21, 102, 188,
References : [1][2]
Queue implementation using linked list in Java 18 Feb 2014 12:50 AM (11 years ago)
package com.krish.queue;
import com.krish.datastructures.common.Cell;
public class QueueMain {
Cell head;
Cell tail;
public QueueMain() {
head = null;
tail = null;
}
public void enqueue(Object obj) {
Cell newCell = new Cell(obj, null);
if (head == null && tail == null)
head = newCell;
else
tail.next = newCell;
tail = newCell;
System.out.println("Enqueud element:"+obj);
printQueue();
}
public Cell front() {
return head;
}
public Cell rear() {
return tail;
}
public void dequeue() {
if (head == null && tail == null) {
System.out.println("Q is empty");
} else {
System.out.println("Dequeued element:"+head.getVal());
if (head.next == null) {
tail = null;
}
head = head.next;
}
printQueue();
}
public int getsize() {
int size = 0;
if(!(head ==null && tail == null)){
size = 1;
for(Cell n = head; n.next != null; n = n.next)
size = size+1;
return size;
}
return size;
}
public void printQueue() {
if (head == null && tail == null) {
System.out.println("Q is empty");
} else {
System.out.println("Q Elememts:");
Cell current = head;
System.out.println("Head");
while (current != null) {
System.out.println("->" + current.getVal());
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("<--tail br=""> System.out.println("Size of the Q:"+getsize());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueMain queue = new QueueMain();
queue.enqueue(23);
queue.enqueue(43);
queue.enqueue(143);
queue.enqueue(321);
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
}
}
Q Elememts:
Head
->23
<--tail br="">Size of the Q:1
Enqueud element:43
Q Elememts:
Head
->23
->43
<--tail br="">Size of the Q:2
Enqueud element:143
Q Elememts:
Head
->23
->43
->143
<--tail br="">Size of the Q:3
Enqueud element:321
Q Elememts:
Head
->23
->43
->143
->321
<--tail br="">Size of the Q:4
Dequeued element:23
Q Elememts:
Head
->43
->143
->321
<--tail br="">Size of the Q:3
Dequeued element:43
Q Elememts:
Head
->143
->321
<--tail br="">Size of the Q:2
References : [1][2][3][4]
Stack implementation using linked list in Java 17 Feb 2014 4:40 AM (11 years ago)
package com.krish.datastructures.common;
public class Cell {
Object val; // value in the cell
public Cell next; // the address of the next cell in the list
/**
* Constructor Cell builds a new cell
*
* @param value
* - the value inserted in the cell
* @param link
* - the cell that is chained to this new cell
*/
public Cell(Object value, Cell link) {
val = value;
next = link;
}
/** getVal returns the value held in the cell */
public Object getVal() {
return val;
}
/** getNext returns the address of the cell chained to this one */
public Cell getNext() {
return next;
}
/**
* setNext resets the address of the cell chained to this one
*
* @param link
* - the address of the Cell that is chained to this one
*/
public void setNext(Cell link) {
next = link;
}
}
package com.krish.stack;
import com.krish.datastructures.common.Cell;
public class StackUsingLinkedLists {
public static Cell top;
/** Constructor Stack creates an empty stack */
public StackUsingLinkedLists() {
top = null;
}
/**
* push inserts a new element onto the stack
*
* @param ob
* - the element to be added
*/
public void push(Object ob) {
System.out.println("PUSH : Inserted the element:" + ob);
top = new Cell(ob, top);
printStack();
}
/**
* pop removes the most recently added element prints error if stack is
* empty
*/
public void pop() {
if (top == null) {
System.out.println("POP: Stack error: stack empty");
} else {
Object answer = top.getVal();
top = top.getNext();
System.out.println("POP: popped the element:" + answer);
printStack();
}
}
/**
* top returns the identity of the most recently added element
*
* @return the element
* @exception RuntimeException
* if stack is empty
*/
public Object top() {
if (top == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stack error: stack empty");
}
return top.getVal();
}
/**
* isEmpty states whether the stack has 0 elements.
*
* @return whether the stack has no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (top == null);
}
// Print the stack elements by using top and next
public void printStack() {
if (top == null) {
System.out.println("PRINT: Stack error: stack empty");
} else {
System.out.println("PRINT:These are the stack elements now!");
Cell temp = top;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.println(temp.getVal());
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StackUsingLinkedLists stack = new StackUsingLinkedLists();
stack.pop();
stack.push(23);
stack.push(267);
stack.push(500);
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
}
}
PUSH : Inserted the element:23
PRINT:These are the stack elements now!
23
PUSH : Inserted the element:267
PRINT:These are the stack elements now!
267
23
PUSH : Inserted the element:500
PRINT:These are the stack elements now!
500
267
23
POP: popped the element:500
PRINT:These are the stack elements now!
267
23
POP: popped the element:267
PRINT:These are the stack elements now!
23
POP: popped the element:23
PRINT: Stack error: stack empty
Stack implementation in Java 17 Feb 2014 12:15 AM (11 years ago)

Stack : Stack in first in last out operated data structure ,where the first inserted (push'ed)element into the stack will be taken out (pop'ed) at last. it is like single door room . Those who enters room first will be able to come out only in the last . In other word last pushed element will be poped out first .
which we call generally as LIFO - Last In First Out
We can implement this stack using Java arrays like below ...
The below implementation takes/reads size of the stack what user want to create and implements stack operations.
Main Program :
package com.krish.stack;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class StackMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String size;
System.out.println("Enter stack size u want to create : ");
size = br.readLine();
System.out.println("Creating a Stack size is:"+Integer.parseInt(size));
Stack stack = new Stack(Integer.parseInt(size));
stack.printStackElements();
stack.push(100);
stack.push(200);
stack.push(300);
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Stack Class: package com.krish.stack;
public class Stack {
int[] myStack;
int top = -1;
int size;
public Stack(int size) {
this.size = size;
myStack = new int[size];
}
public void printStackElements() {
if (top >= 0) {
System.out.println("Present elements in the stack:");
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
System.out.println("Element at " + i + "position is "
+ myStack[i]);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
}
}
public void push(int element) {
if (top < size - 1) {
System.out.println("Pushing " + element + " to stack now");
System.out.println("After push()");
top++;
myStack[top] = element;
printStackElements();
} else {
System.out.println("Stack overflow; element can't be pushed");
}
}
public void pop() {
if (top >= 0) {
System.out.println("Poping the top element now:" + myStack[top]);
top--;
printStackElements();
} else {
System.out.println("stack undeflow");
}
}
}
Output : Enter stack size u want to create :
2
Creating a Stack size is:2
Stack is empty
Pushing 100 to stack now
After push()
Present elements in the stack:
Element at 0position is 100
Pushing 200 to stack now
After push()
Present elements in the stack:
Element at 0position is 100
Element at 1position is 200
Stack overflow; element can't be pushed
Poping the top element now:200
Present elements in the stack:
Element at 0position is 100
Poping the top element now:100
Stack is empty
stack undeflow
Advantages and disadvanaatages of using arrays in this :
1. We can access any stack element when in array at any point of time randomly.
2. Size is fixed we can't add more elements.
3. If we want to remove an element in between the elements then it is difficult to adjust the other elements.
4. IF we want to insert at a particular position in between the array also it is difficult.
Reference : [1]
SQL injection - Java 16 Feb 2014 9:58 PM (11 years ago)
SQL injection is a code injection technique, used to attack data driven applications, in which malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field for execution (e.g. to dump the database contents to the attacker).[1] SQL injection must exploit a security vulnerability in an application's software, for example, when user input is either incorrectly filtered for string literal escape characters embedded in SQL statements or user input is not strongly typed and unexpectedly executed. SQL injection is mostly known as an attack vector for websites but can be used to attack any type of SQL database.
PreparedStatements are the way to go, because they make SQL injection impossible. Here's a simple example taking the user's input as the parameters:
public insertUser(String name, String email) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
try {
conn = setupTheDatabaseConnectionSomehow();
stmt = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO person (name, email) values (?, ?)");
stmt.setString(1, name);
stmt.setString(2, email);
stmt.executeUpdate();
}
finally {
try {
if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); }
}
catch (Exception e) {
// log this error
}
try {
if (conn != null) { conn.close(); }
}
catch (Exception e) {
// log this error
}
}
}
Reference :
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1812891/java-escape-string-to-prevent-sql-injection
JDBC - Java - Interview questions 16 Feb 2014 9:51 PM (11 years ago)
Establishing a connection. : First, establish a connection with the data source you want to use. A data source can be a DBMS, a legacy file system, or some other source of data with a corresponding JDBC driver. This connection is represented by a Connection object.
Create a statement. : A Statement is an interface that represents a SQL statement. You execute Statement objects, and they generate ResultSet objects, which is a table of data representing a database result set. You need a Connection object to create a Statement object.
There are three different kinds of statements:
Statement: Used to implement simple SQL statements with no parameters.
PreparedStatement: (Extends Statement.) Used for precompiling SQL statements that might contain input parameters. See Using Prepared Statements for more information.
CallableStatement: (Extends PreparedStatement.) Used to execute stored procedures that may contain both input and output parameters. See Stored Procedures for more information.
Execute the query. :
To execute a query, call an execute method from Statement such as the following:
execute: Returns true if the first object that the query returns is a ResultSet object. Use this method if the query could return one or more ResultSet objects. Retrieve the ResultSet objects returned from the query by repeatedly calling Statement.getResultSet.
executeQuery: Returns one ResultSet object.
executeUpdate: Returns an integer representing the number of rows affected by the SQL statement. Use this method if you are using INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE SQL statements.
Process the ResultSet object. : You access the data in a ResultSet object through a cursor. Note that this cursor is not a database cursor. This cursor is a pointer that points to one row of data in the ResultSet object. Initially, the cursor is positioned before the first row. You call various methods defined in the ResultSet object to move the cursor.
Close the connection. : When you are finished using a Statement, call the method Statement.close to immediately release the resources it is using. When you call this method, its ResultSet objects are closed.
For example, the method CoffeesTables.viewTable ensures that the Statement object is closed at the end of the method, regardless of any SQLException objects thrown, by wrapping it in a finally block:
} finally {
if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); }
}
JDBC throws an SQLException when it encounters an error during an interaction with a data source.
DB2 - GROUP BY - HAVING 6 Jan 2014 8:48 PM (11 years ago)
TOUR_GROUP : Table has following coloumns
SELECT LANGUAGE, COUNT(*) "NUMBER_OF_TOURS", MAX(GROUP_SIZE) "MAX_GROUP_SIZE", MIN(GROUP_SIZE) "MIN_GROUP_SIZE"
FROM TOUR_GROUP
GROUP BY LANGUAGE
ORDER BY NUMBER_OF_TOURS;
Query 2 :
FROM TOUR_GROUP
WHERE GROUP_SIZE <= 20
GROUP BY LANGUAGE
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
ORDER BY NUMBER_OF_TOURS;
FROM TOUR_GROUP
GROUP BY TOUR
ORDER BY COUNT(DISTINCT LANGUAGE), TOUR;


